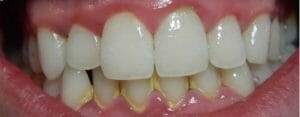
Untreated gum disease poses a serious risk to your oral health. If you notice signs of gum issues, contact your dentist to schedule an appointment.
Gum disease affects millions of people across the United States. In 2012, the CDC released a report that showed almost half of Americans over the age of 30 show signs of gum disease. Oftentimes, people don’t even notice the symptoms until they visit their dentist for an oral exam.
Your oral health is a single part of a larger system. Moreover, oral health issues have an impact on the entire body. When we neglect our oral health, it leads to gum disease.
In turn, untreated gum disease has the potential to progress into a life-threatening health condition. Below, we look at a few health conditions to help you understand the importance of maintaining your oral health.
What Causes Gum Disease?
Typically, the buildup of tartar and plaque starts the progression towards gum disease. Then, they release toxins that infect both the tissue of the gums and bone structure. Over time, this has the potential to cause chronic inflammation and even tooth loss.
In many cases, young patients don’t show signs of gum disease. This is because the early stages of infection tend to be painless. However, the symptoms become more prevalent in adulthood.
Common Signs of Gum Disease
- Bad breath
- Bleeding in the gums
- Inflamed, red gums
- Loose teeth
- Pain when you chew
- Receding gum line
- Sensitivity in the teeth
Untreated Gum Disease Can Trigger Life-Threatening Conditions
Early on, untreated gum disease begins as inflammation. Periodontal disease (gum disease) is the chronic inflammation of the gums, and it requires continued care. Unfortunately, there’s no way to reverse it.
However, it’s possible to manage the condition. When you do, you help to prevent other life-threatening conditions.
Heart Disease
Chronic inflammation is the enemy of the human body. When the body begins to attack healthy cells, it becomes a problem. This is also the reason why people link gum disease to heart disease.
- Gum disease has a negative impact on the blood pressure of hypertensive individuals. Moreover, it disrupts the effects of hypertension medicines.
- According to the American Heart Association, those with poor dental health are more prone to heart disease.
- Researchers found that gum disease increases someone’s risk of heart attack by nearly 50%.
Inflammation in the gums directly relates to inflammation in the heart. However, when you treat gum disease, it has the potential to decrease the blood pressure in some patients.
As Houston dentists, we encourage our patients to visit us frequently in order to monitor gum disease. Moreover, we strive to keep them aware of the risks of untreated gum disease and how to reverse early stages.
Diabetes
Generally, bacteria thrive when around sugar. With high glucose levels in the body, bacteria propagate. This fuels the germs to attack the gums and teeth.
Additionally, periodontal disease increases the levels of blood sugar. This has the potential to put people at risk for Type 2 Diabetes.
How does gum disease increase blood sugar?
When the bacteria that infect gum tissue leak into the bloodstream, it causes a stir in your body’s immune system. To defend itself, your body triggers a rise in blood sugar in order to fight off the bacteria.
Because untreated gum disease leads to chronic inflammation, it is more difficult to control blood sugar levels. Similarly, diabetes makes it hard for the body to fight off infections, including periodontal disease.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
There is a bacteria found in patients of both rheumatoid arthritis and gum disease: Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. This bacteria triggers an inflammatory autoimmune response in the body.
In turn, this makes the proteins in the immune system overactive. Thus, it causes joint inflammation.
Alzheimer’s Disease
There’s also a link between gum disease and a patient’s risk for Alzheimer’s According to this study, the bacteria Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. gingivalis) is common in both gum disease and Alzheimer’s patients.
This neurodegenerative disease impacts 5 million Americans. It begins with the loss of memory and worsens over time. Moreover, experts warn that in order to avoid complications such as this, it is crucial to prevent gum disease. This is because the bacteria tend to infiltrate the body.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia and asthma also bear an impact from the chronic inflammation from gum disease. According to the American Thoracic Society, the infection in the gums triggers a high alert status in the immune system. Then, it ensures inflammation across the body.
Unfortunately, this impacts the lungs and airways. As a result, it puts people at risk for a broad spectrum of respiratory conditions, including Coronavirus. When you work to maintain healthy gums, you help to avoid inflammation throughout your body.
Untreated Gum Disease: Monitor Oral Health with Your Dentist
Understanding the impact of untreated gum disease is a great start. However, it’s better to schedule an appointment with your dentist. It’s never too later to understand your dental and periodontal health.
That’s why it’s essential to visit your dentist for regular exams and periodontal treatments. Be mindful of the slow, silent onset of untreated gum disease and book an appointment with your dentist.
While there’s no way to reverse late gum disease, there’s the potential to manage the impact. As you brush and floss your teeth, remember that it impacts more than just your oral health. Regular, proper dental care helps to protect your body.